person who has been granted lawful permanent residence in the United States. Permanent resident status confers certain rights and responsibilities.
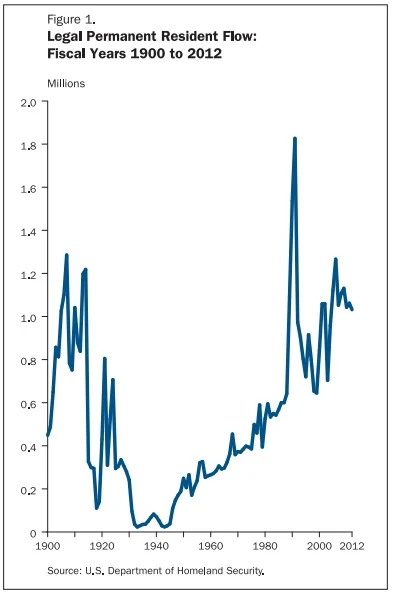
The annual LPR flow has exhibited an upward trend since 1945 (see Figure 1). The average annual LPR flow increased from 250,000 during the 1950s to more than 1 million between 2000 and 2012. Changes in immigration law associated with this increase included the elimination of country quotas controlling Eastern Hemisphere immigration, increases in annual limits for hemispheric and preference immigration, and the inclusion of parents of adult U.S. citizens as numerically exempt immediate relatives.
The spike in legal immigration around 1990 reflects the legalization of 2.7 million unauthorized immigrants under the Immigration Reform and Control Act (IRCA) of 1986.
Legal Permanent Resident Flow: Fiscal Years 2010 to 2012:
| Category of admission | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | |||
| Number | Percent | Number | Percent | Number | Percent | |
| Total | 1,031,631 | 100 | 1,062,040 | 100 | 1,042,625 | 100 |
| New arrivals | 484,072 | 46.9 | 481,948 | 45.4 | 476,049 | 45.7 |
| Adjustments of status | 547,559 | 53.1 | 580,092 | 54.6 | 566,576 | 54.3 |
Legal Permanent Resident Flow by Major Category of Admission: Fiscal Years 2010 to 2012
| Category of admission | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | |||
| Number | Percent | Number | Percent | Number | Percent | |
| Total | 1,031,631 | 100 .0 | 1,062,040 | 100 .0 | 1,042,625 | 100 .0 |
| Family-sponsored immigrants | 680,799 | 66 .0 | 688,089 | 64 .8 | 691,003 | 66 .3 |
| Family sponsored preferences | 202,019 | 19 .6 | 234,931 | 22 .1 | 214,589 | 20 .6 |
| (a) Unmarried sons/daughters of U .S . Citizens | 20,660 | 2 .0 | 27,299 | 2 .6 | 26,998 | 2 .6 |
| (b) Spouses and children of alien residents | 99,709 | 9 .7 | 108,618 | 10 .2 | 92,088 | 8 .8 |
| (c) Married sons/daughters of U .S . Citizens | 21,752 | 2 .1 | 27,704 | 2 .6 | 32,817 | 3 .1 |
| (d) Siblings of U .S . Citizens | 59,898 | 5 .8 | 71,310 | 6 .7 | 62,686 | 6 .0 |
| Immediate relatives of U .S . Citizens | 478,780 | 46 .4 | 453,158 | 42 .7 | 476,414 | 45 .7 |
| (a) Spouses | 273,429 | 26 .5 | 258,320 | 24 .3 | 271,909 | 26 .1 |
| (b) Parents | 124,230 | 12 .0 | 114,527 | 10 .8 | 116,208 | 11 .1 |
| (c) Children | 81,121 | 7 .9 | 80,311 | 7 .6 | 88,297 | 8 .5 |
| Employment-based preferences | 143,998 | 14 .0 | 139,339 | 13 .1 | 148,343 | 14 .2 |
| Priority workers | 39,316 | 3 .8 | 25,251 | 2 .4 | 41,055 | 3 .9 |
| Professionals with advanced degrees | 50,959 | 4 .9 | 66,831 | 6 .3 | 53,946 | 5 .2 |
| Skilled workers, professionals, unskilled workers | 39,229 | 3 .8 | 37,216 | 3 .5 | 39,762 | 3 .8 |
| Special immigrants | 7,866 | 0 .8 | 6,701 | 0 .6 | 11,100 | 1 .1 |
| Investors | 6,628 | 0 .6 | 3,340 | 0 .3 | 2,480 | 0 .2 |
| Diversity programs | 40,320 | 3 .9 | 50,103 | 4 .7 | 49,763 | 4 .8 |
| Refugees and Asylees | 150,614 | 14 .6 | 168,460 | 15 .9 | 136,291 | 13 .1 |
| Refugee adjustments | 105,528 | 10 .2 | 113,045 | 10 .6 | 92,741 | 8 .9 |
| Asylee adjustments | 45,086 | 4 .4 | 55,415 | 5 .2 | 43,550 | 4 .2 |
| Parolees | 758 | 0 .1 | 1,147 | 0 .1 | 1,592 | 0 .2 |
| Other categories | 15,142 | 1 .5 | 14,902 | 1 .4 | 15,633 | 1 .5 |
| (a) Children born abroad to alien residents | 643 | 0 .1 | 633 | 0 .1 | 716 | 0 .1 |
| (b) NACARA † Section 202 | 183 | — | 158 | — | 248 | — |
| (c) Cancellation of removal | 6,818 | 0 .7 | 7,430 | 0 .7 | 8,180 | 0 .8 |
| Subject to annual limit | 4,015 | 0 .4 | 4,206 | 0 .4 | 4,475 | 0 .4 |
| Not subject to limit (NACARA† Section 203) | 2,803 | 0 .3 | 3,224 | 0 .3 | 3,705 | 0 .4 |
| (d) Haitian Refugee Immigrant Fairness Act | 93 | — | 154 | — | 386 | — |
| (e) Other | 7,405 | 0 .7 | 6,527 | 0 .6 | 6,103 | 0 .6 |
Paths to LPR Status:
There are two paths to LPR status depending on whether the applicant is living in the United States or another country at the time of application. Foreign nationals living abroad apply for an immigrant visa at a consular office of the Department of State. Once issued a visa, a foreign national may enter the United States and become an LPR when admitted at a port of entry. These LPRs are referred to as new arrivals in this report.
Persons who qualify for legal permanent resident status who are living in the United States, including refugees, asylees, and certain temporary workers, foreign students, family members of U.S. citizens or alien residents, and undocumented immigrants, file an application for adjustment of status to lawful permanent residence with U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS). At the time they apply for adjustment of status, they may also apply for permission to work. Adjustment of status applicants are granted lawful permanent residence at the time their applications are approved. These LPRs are referred to as adjustments of status in this report.
Continue to Part 2: http://blog.mygcvisa.com/2013/03/green-card-processing-statistics-part-2.html
how can someone knw whether he /she has got agreencard to the us
ReplyDeleteThat question is too intelligent for anyone in the world to answer
Delete